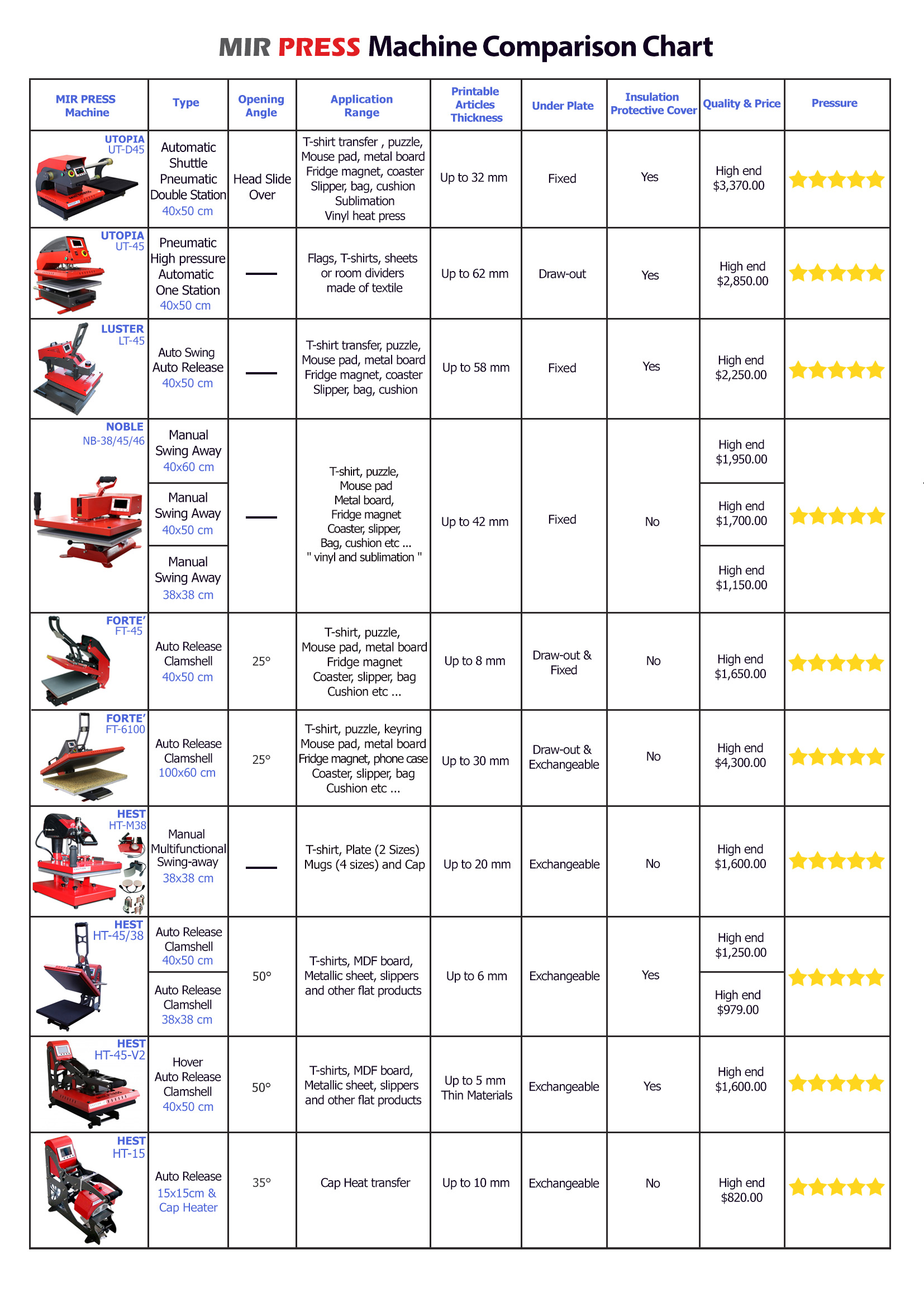
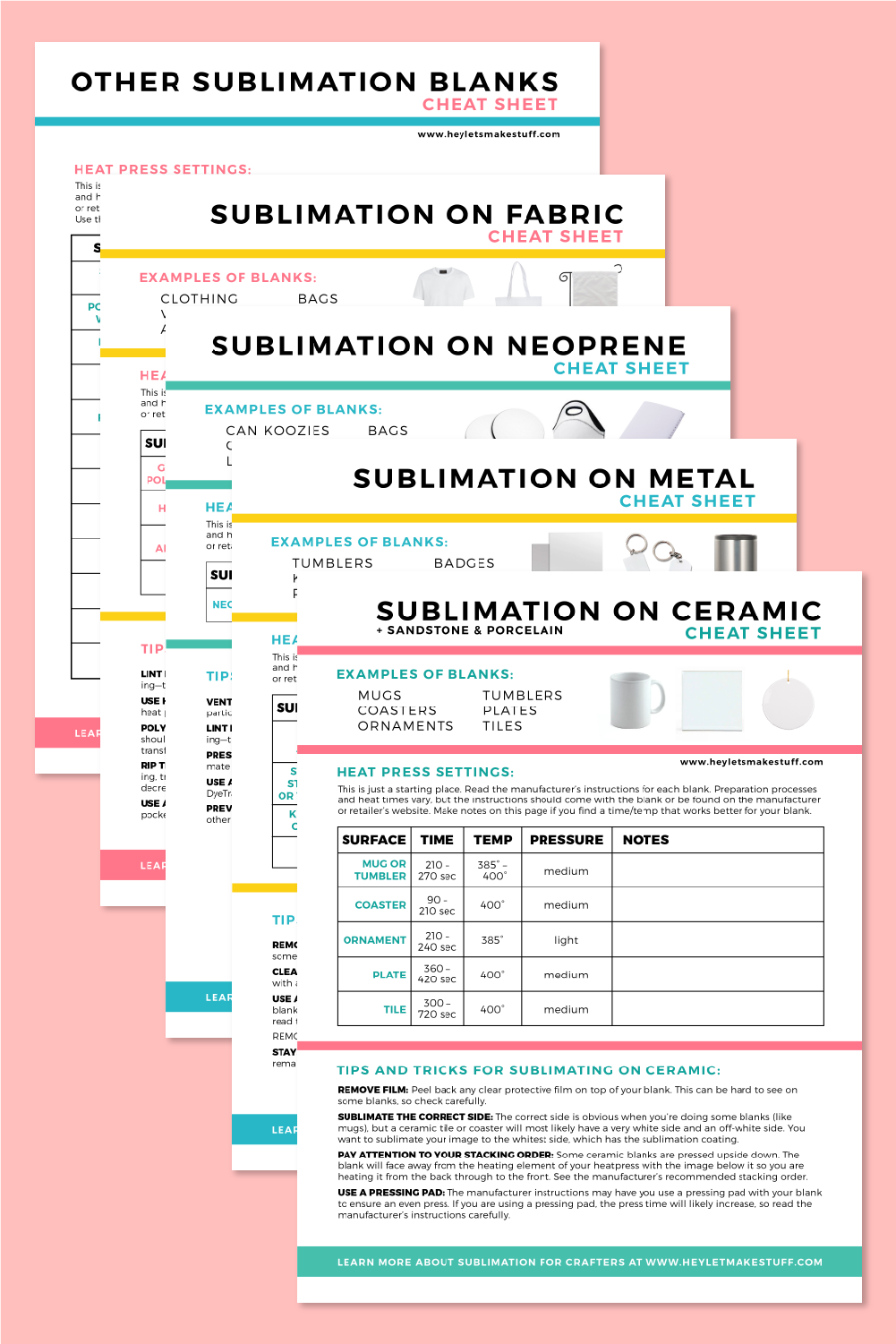
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide - Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase under specific conditions of temperature and. When dry ice is placed in contact with air, it gets converted into the gaseous carbon dioxide which. Sublimation is a physical process. Sublimation is the transition from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. This endothermic phase transition occurs at. An example is the vaporization of frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice) at ordinary. Sublimation or sublimate may refer to: Sublimation is the process of changing a solid into a gas directly. Sublimation is caused by the absorption of heat which provides enough energy for some molecules to overcome the attractive forces of their neighbors and escape into the vapor. Examples of sublimation are dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. Sublimation or sublimate may refer to: This endothermic phase transition occurs at. When dry ice is placed in contact with air, it gets converted into the gaseous carbon dioxide which. It is similar to when the ice cubes evaporate without even melting into the water. Examples of sublimation are dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. Sublimation is the process of changing a solid into a gas directly. Sublimation is the process by which a substance transitions directly from the solid phase to the gaseous phase, bypassing the liquid phase. Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase under specific conditions of temperature and. Sublimation, in physics, conversion of a substance from the solid to the gaseous state without its becoming liquid. Sublimation is the conversion between the solid and the gaseous phases of matter, with no intermediate liquid stage. Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase under specific conditions of temperature and. Sublimation is caused by the absorption of heat which provides enough energy for some molecules to overcome the attractive forces of their neighbors and escape into the vapor. When dry ice. Sublimation is the process by which a substance transitions directly from the solid phase to the gaseous phase, bypassing the liquid phase. Sublimation is the transition from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. An example is the vaporization of frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice) at ordinary. Examples of sublimation are dry ice. Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase under specific conditions of temperature and. Sublimation is a physical process. Sublimation (album), by canvas solaris, 2004 sublimation (phase transition), directly from the solid to the gas phase sublimation (psychology), a mature. Sublimation or sublimate may refer. Sublimation, in physics, conversion of a substance from the solid to the gaseous state without its becoming liquid. Examples of sublimation are dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is similar to when the ice cubes evaporate without even melting into the water. Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the. Sublimation is the conversion between the solid and the gaseous phases of matter, with no intermediate liquid stage. Sublimation or sublimate may refer to: Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase under specific conditions of temperature and. For those of us interested in the. Sublimation is the transition from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. When dry ice is placed in contact with air, it gets converted into the gaseous carbon dioxide which. Examples of sublimation are dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. Sublimation or sublimate may refer to: Sublimation is caused by. Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase under specific conditions of temperature and. Sublimation is the transition from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. For those of us interested in the water cycle, sublimation is. It. An example is the vaporization of frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice) at ordinary. Sublimation or sublimate may refer to: This endothermic phase transition occurs at. Sublimation is the process of changing a solid into a gas directly. When dry ice is placed in contact with air, it gets converted into the gaseous carbon dioxide which. Sublimation is caused by the absorption of heat which provides enough energy for some molecules to overcome the attractive forces of their neighbors and escape into the vapor. An example is the vaporization of frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice) at ordinary. Sublimation is a physical process. Sublimation is the process of changing a solid into a gas directly. When dry. Sublimation is the transition from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. Examples of sublimation are dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. Sublimation (album), by canvas solaris, 2004 sublimation (phase transition), directly from the solid to the gas phase sublimation (psychology), a mature. For those of us interested in the. This endothermic phase transition occurs at. Sublimation is the process of changing a solid into a gas directly. An example is the vaporization of frozen carbon dioxide (dry ice) at ordinary. Sublimation is caused by the absorption of heat which provides enough energy for some molecules to overcome the attractive forces of their neighbors and escape into the vapor. Sublimation is a physical process. It is similar to when the ice cubes evaporate without even melting into the water. Sublimation or sublimate may refer to: Sublimation (album), by canvas solaris, 2004 sublimation (phase transition), directly from the solid to the gas phase sublimation (psychology), a mature. Sublimation is the transition from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through an intermediate liquid phase. For those of us interested in the water cycle, sublimation is. Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid phase to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase under specific conditions of temperature and. Sublimation, in physics, conversion of a substance from the solid to the gaseous state without its becoming liquid.Heat Press Temperature Guide Sublimation and HTV Heat press, Sublime
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide
Sublimation Time and Temperature Guide, Digital Download, Instant
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide
Sublimation Temperature Chart Printable Essential Heat Settings Guide
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide
Sublimation Printable Heat Press Temperature Guide
Sublimation Is The Process By Which A Substance Transitions Directly From The Solid Phase To The Gaseous Phase, Bypassing The Liquid Phase.
When Dry Ice Is Placed In Contact With Air, It Gets Converted Into The Gaseous Carbon Dioxide Which.
Examples Of Sublimation Are Dry Ice Is The Solid Form Of Carbon Dioxide.
Sublimation Is The Conversion Between The Solid And The Gaseous Phases Of Matter, With No Intermediate Liquid Stage.
Related Post: