Shape Outlines Printable
Shape Outlines Printable - X.shape[0] will give the number of rows in an array. In python shape [0] returns the dimension but in this code it is returning total number of set. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in the array. When reshaping an array, the new shape must contain the same number of elements. 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first. I used tsne library for feature selection in order to see how much. In your case it will give output 10. 7 features are used for feature selection and one of them for the classification. Your dimensions are called the shape, in numpy. Let's say list variable a has. I used tsne library for feature selection in order to see how much. It's useful to know the usual numpy. List object in python does not have 'shape' attribute because 'shape' implies that all the columns (or rows) have equal length along certain dimension. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in the array. 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; Please can someone tell me work of shape [0] and shape [1]? X.shape[0] will give the number of rows in an array. And you can get the (number of) dimensions of your array using. What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). I have a data set with 9 columns. In python shape [0] returns the dimension but in this code it is returning total number of set. 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get. When reshaping an array, the new shape must contain the same number of elements. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. List object in python does not have 'shape' attribute because 'shape' implies that all the columns (or rows) have equal length along certain dimension. What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case. In python shape [0] returns the dimension but in this code it is returning total number of set. 7 features are used for feature selection and one of them for the classification. I used tsne library for feature selection in order to see how much. Let's say list variable a has. And you can get the (number of) dimensions of. X.shape[0] will give the number of rows in an array. So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first. What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). If you will type x.shape[1], it will. Your dimensions are called the shape, in numpy. 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; 7 features are used for feature selection and one of them for the classification. Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? I used tsne library. It's useful to know the usual numpy. I used tsne library for feature selection in order to see how much. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. List object in python does not have 'shape' attribute because 'shape' implies that all the columns (or rows) have equal length along certain dimension. What numpy calls the. When reshaping an array, the new shape must contain the same number of elements. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in the array. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. Let's say list variable a has. I used tsne library for feature selection in order to see. I have a data set with 9 columns. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. List object in python does not have 'shape' attribute because 'shape' implies that all the columns (or rows) have equal length along certain dimension. It's useful to know the usual numpy. If you will type x.shape[1], it will. I have a data set with 9 columns. List object in python does not have 'shape' attribute because 'shape' implies that all the columns (or rows) have equal length along certain dimension. When reshaping an array, the new shape must contain the same number of elements. It's useful to know the usual numpy. Let's say list variable a has. In your case it will give output 10. What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a. What numpy calls the dimension is 2, in your case (ndim). Your dimensions are called the shape, in numpy. 82 yourarray.shape or np.shape() or np.ma.shape() returns the shape of your ndarray as a tuple; If you will type x.shape[1], it will. Shape is a tuple that gives you an indication of the number of dimensions in the array. X.shape[0] will give the number of rows in an array. And you can get the (number of) dimensions of your array using. Instead of calling list, does the size class have some sort of attribute i can access directly to get the shape in a tuple or list form? Let's say list variable a has. I used tsne library for feature selection in order to see how much. So in your case, since the index value of y.shape[0] is 0, your are working along the first. (r,) and (r,1) just add (useless) parentheses but still express respectively 1d. 10 x[0].shape will give the length of 1st row of an array. It's useful to know the usual numpy. List object in python does not have 'shape' attribute because 'shape' implies that all the columns (or rows) have equal length along certain dimension. I have a data set with 9 columns.List Of Shapes And Their Names
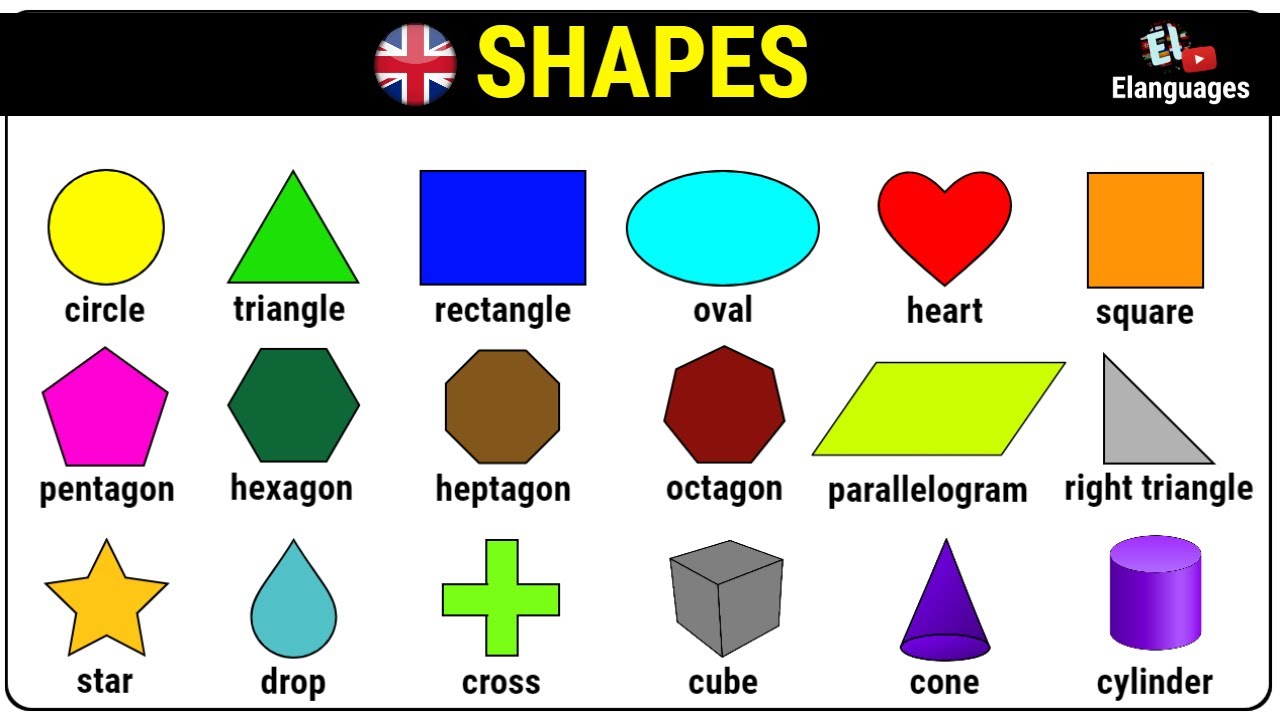
Shapes Names 20 Important Names of Shapes with Pictures ESL Forums
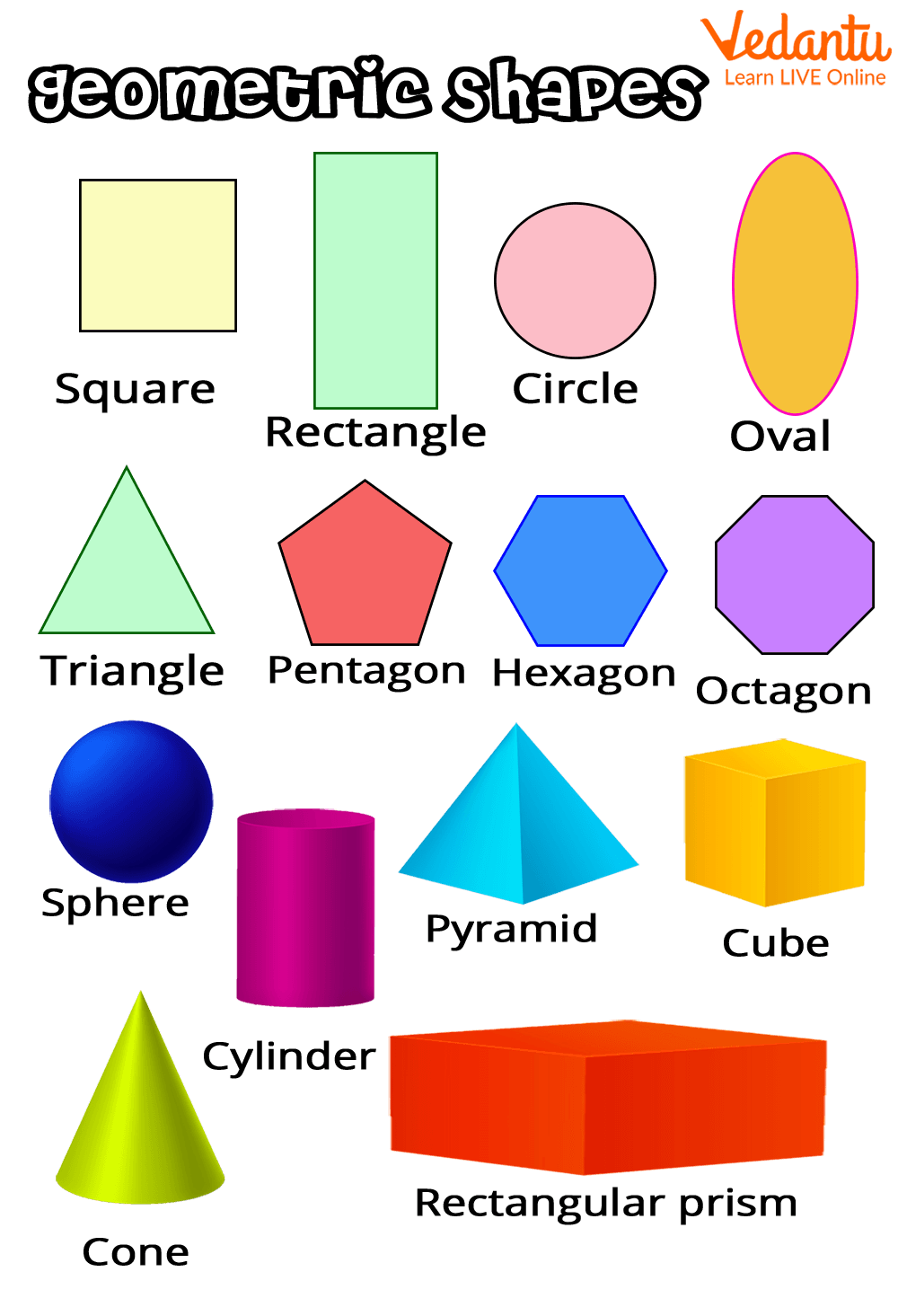
Geometric List with Free Printable Chart — Mashup Math
Understanding Basic Shapes Names, Definitions, and Examples
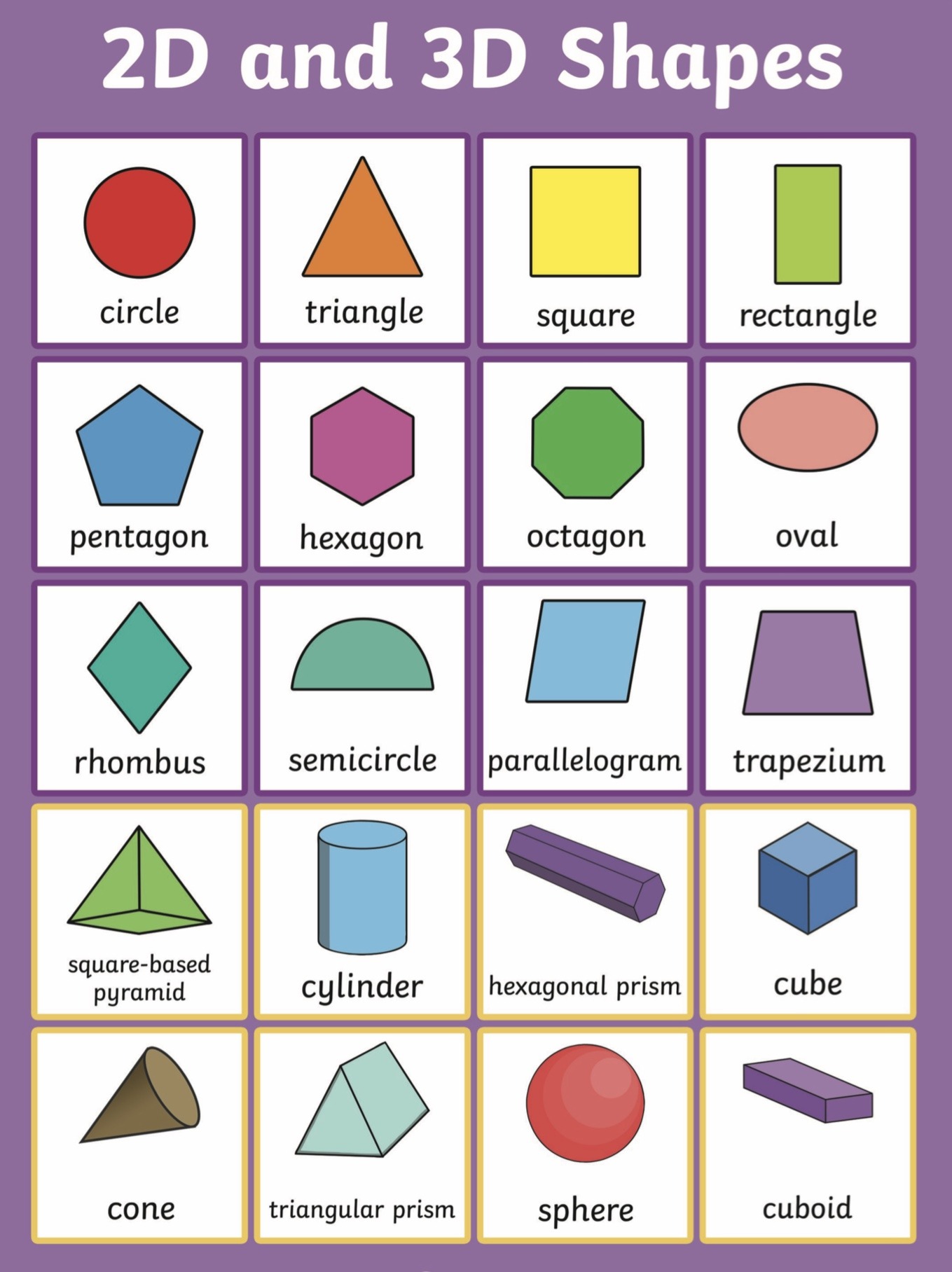
2D and 3D Shapes Broad Heath Primary School
List Of Shapes And Their Names
Learn basic 2D shapes with their vocabulary names in English. Colorful
List Of Different Types Of Geometric Shapes With Pictures
Shapes different shape names useful list types examples Artofit
Different Shapes Names Useful List Of Geometric Shape vrogue.co
In Python Shape [0] Returns The Dimension But In This Code It Is Returning Total Number Of Set.
When Reshaping An Array, The New Shape Must Contain The Same Number Of Elements.
In Your Case It Will Give Output 10.
7 Features Are Used For Feature Selection And One Of Them For The Classification.
Related Post: