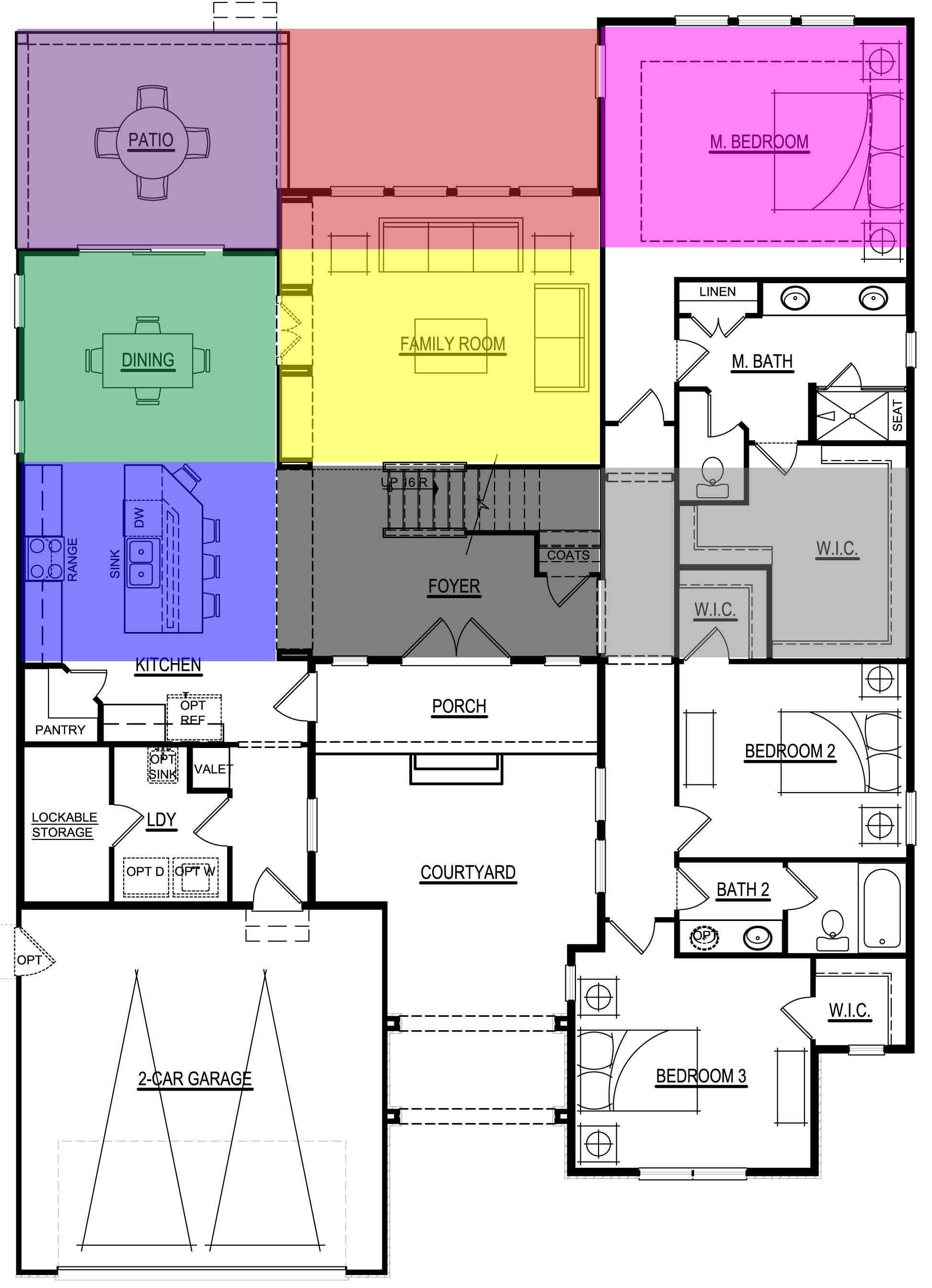
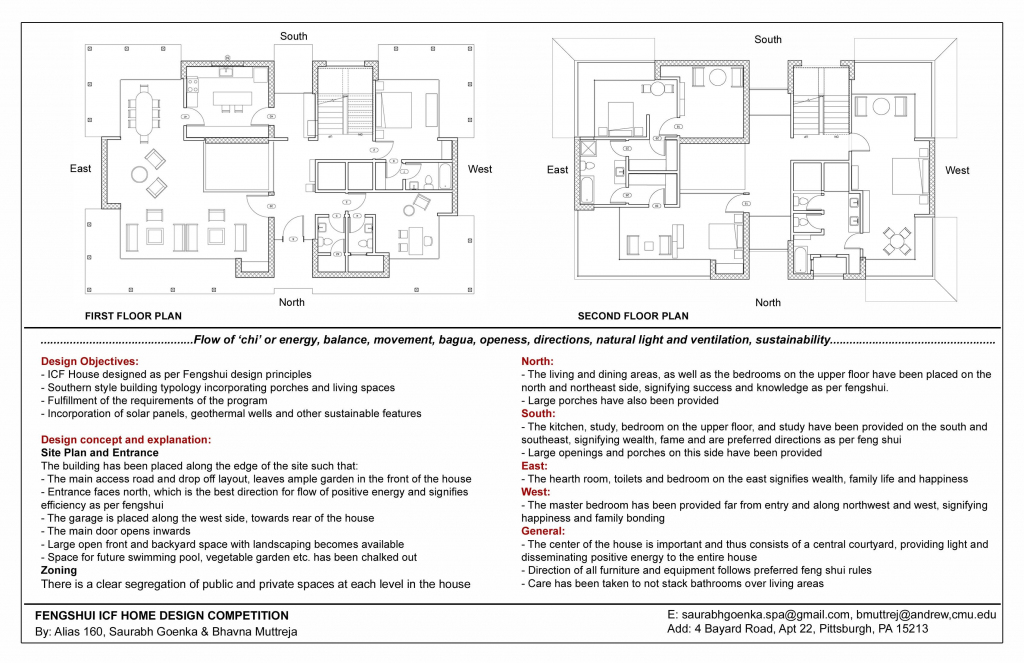
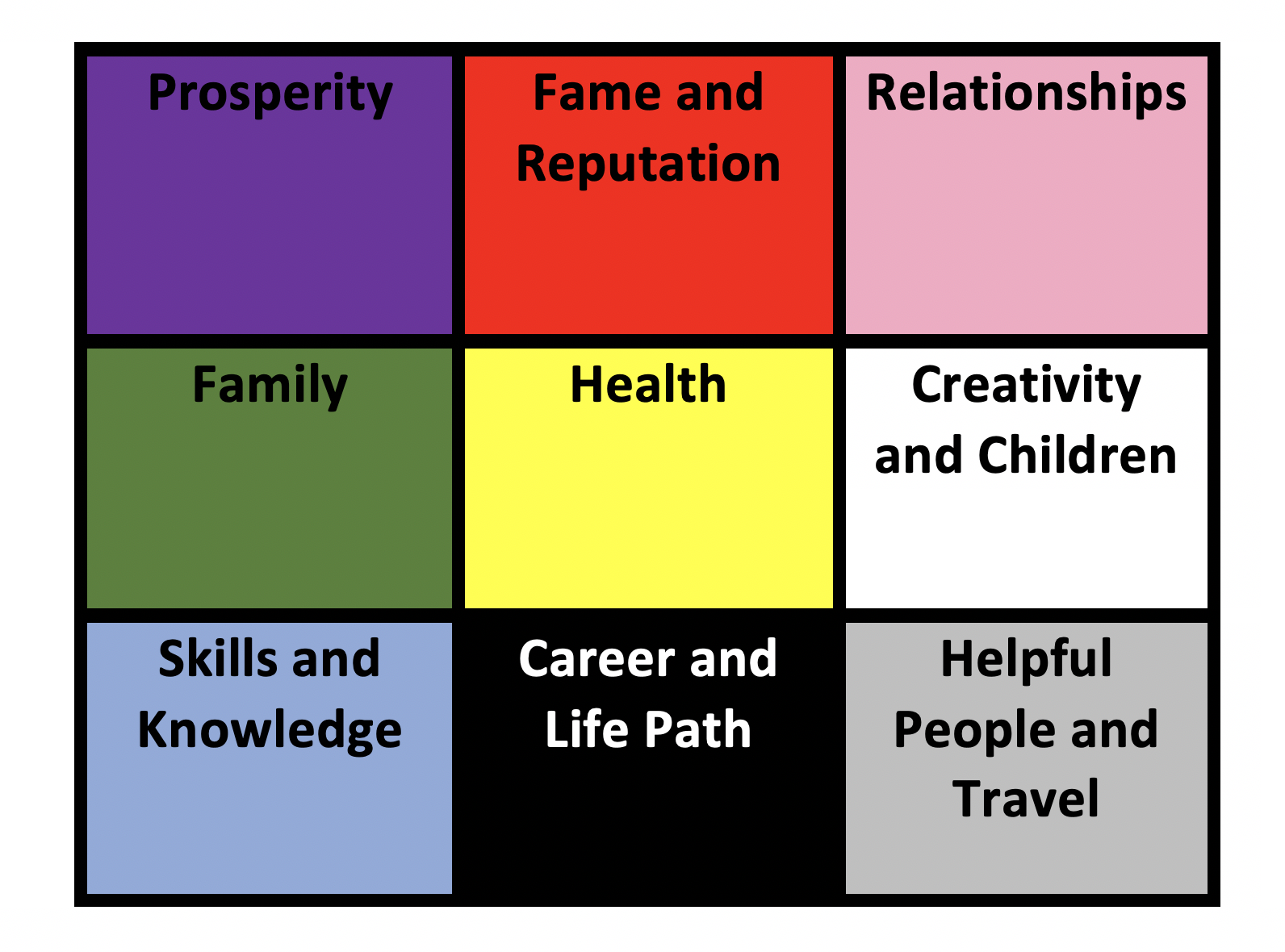
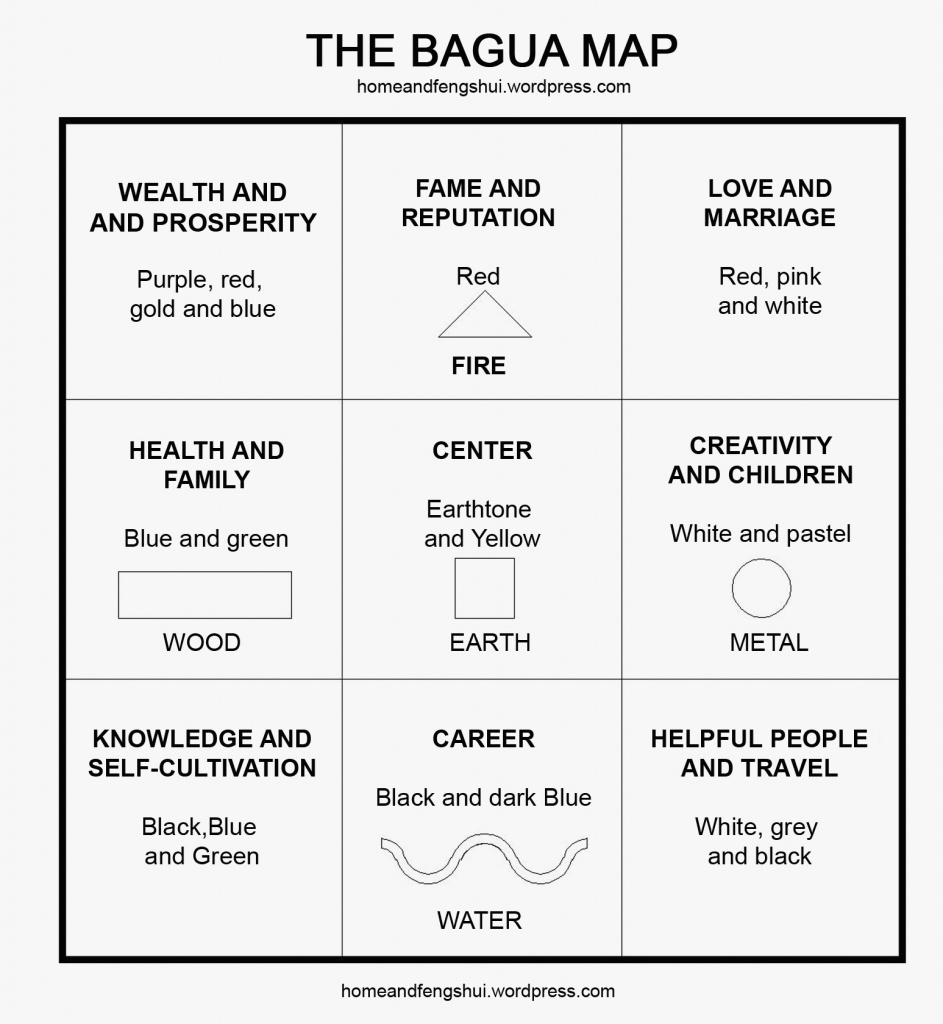
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map - The floor function turns continuous integration problems in to discrete problems, meaning that while you are still looking for the area under a curve all of the curves become rectangles. Taking the floor function means we choose the largest x x for which bx b x is still less than or equal to n n. 17 there are some threads here, in which it is explained how to use \lceil \rceil \lfloor \rfloor. So we can take the. How can we compute the floor of a given number using real number field operations, rather than by exploiting the printed notation,. 4 i suspect that this question can be better articulated as: For example, is there some way to do. But generally, in math, there is a sign that looks like a combination of ceil and floor, which means. At each step in the recursion, we increment n n by one. Try to use the definitions of floor and ceiling directly instead. How can we compute the floor of a given number using real number field operations, rather than by exploiting the printed notation,. Obviously there's no natural number between the two. 17 there are some threads here, in which it is explained how to use \lceil \rceil \lfloor \rfloor. For example, is there some way to do. By definition, ⌊y⌋ = k ⌊ y ⌋ = k if k k is the greatest integer such that k ≤ y. Also a bc> ⌊a/b⌋ c a b c> ⌊ a / b ⌋ c and lemma 1 tells us that there is no natural number between the 2. Now simply add (1) (1) and (2) (2) together to get finally, take the floor of both sides of (3) (3): 4 i suspect that this question can be better articulated as: So we can take the. At each step in the recursion, we increment n n by one. Taking the floor function means we choose the largest x x for which bx b x is still less than or equal to n n. Try to use the definitions of floor and ceiling directly instead. Is there a convenient way to typeset the floor or ceiling of a number, without needing to separately code the left and right parts?. Is there a convenient way to typeset the floor or ceiling of a number, without needing to separately code the left and right parts? For example, is there some way to do. At each step in the recursion, we increment n n by one. Taking the floor function means we choose the largest x x for which bx b x. 4 i suspect that this question can be better articulated as: Try to use the definitions of floor and ceiling directly instead. How can we compute the floor of a given number using real number field operations, rather than by exploiting the printed notation,. So we can take the. Obviously there's no natural number between the two. Also a bc> ⌊a/b⌋ c a b c> ⌊ a / b ⌋ c and lemma 1 tells us that there is no natural number between the 2. But generally, in math, there is a sign that looks like a combination of ceil and floor, which means. The floor function turns continuous integration problems in to discrete problems, meaning that. Obviously there's no natural number between the two. How can we compute the floor of a given number using real number field operations, rather than by exploiting the printed notation,. So we can take the. 17 there are some threads here, in which it is explained how to use \lceil \rceil \lfloor \rfloor. Now simply add (1) (1) and (2). For example, is there some way to do. By definition, ⌊y⌋ = k ⌊ y ⌋ = k if k k is the greatest integer such that k ≤ y. Exact identity ⌊nlog(n+2) n⌋ = n − 2 for all integers n> 3 ⌊ n log (n + 2) n ⌋ = n 2 for all integers n> 3 that. The floor function turns continuous integration problems in to discrete problems, meaning that while you are still looking for the area under a curve all of the curves become rectangles. Your reasoning is quite involved, i think. For example, is there some way to do. So we can take the. Also a bc> ⌊a/b⌋ c a b c> ⌊ a. By definition, ⌊y⌋ = k ⌊ y ⌋ = k if k k is the greatest integer such that k ≤ y. For example, is there some way to do. So we can take the. Taking the floor function means we choose the largest x x for which bx b x is still less than or equal to n n.. Your reasoning is quite involved, i think. 4 i suspect that this question can be better articulated as: Also a bc> ⌊a/b⌋ c a b c> ⌊ a / b ⌋ c and lemma 1 tells us that there is no natural number between the 2. The floor function turns continuous integration problems in to discrete problems, meaning that while. But generally, in math, there is a sign that looks like a combination of ceil and floor, which means. Is there a convenient way to typeset the floor or ceiling of a number, without needing to separately code the left and right parts? By definition, ⌊y⌋ = k ⌊ y ⌋ = k if k k is the greatest integer. Your reasoning is quite involved, i think. By definition, ⌊y⌋ = k ⌊ y ⌋ = k if k k is the greatest integer such that k ≤ y. Taking the floor function means we choose the largest x x for which bx b x is still less than or equal to n n. Exact identity ⌊nlog(n+2) n⌋ = n − 2 for all integers n> 3 ⌊ n log (n + 2) n ⌋ = n 2 for all integers n> 3 that is, if we raise n n to the power logn+2 n log n + 2 n, and take the floor of the. For example, is there some way to do. So we can take the. Is there a convenient way to typeset the floor or ceiling of a number, without needing to separately code the left and right parts? But generally, in math, there is a sign that looks like a combination of ceil and floor, which means. Try to use the definitions of floor and ceiling directly instead. The floor function turns continuous integration problems in to discrete problems, meaning that while you are still looking for the area under a curve all of the curves become rectangles. 17 there are some threads here, in which it is explained how to use \lceil \rceil \lfloor \rfloor. At each step in the recursion, we increment n n by one. How can we compute the floor of a given number using real number field operations, rather than by exploiting the printed notation,.Printable Bagua Map PDF
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Floor Plan Printable Bagua Map
Obviously There's No Natural Number Between The Two.
Now Simply Add (1) (1) And (2) (2) Together To Get Finally, Take The Floor Of Both Sides Of (3) (3):
Also A Bc> ⌊A/B⌋ C A B C> ⌊ A / B ⌋ C And Lemma 1 Tells Us That There Is No Natural Number Between The 2.
4 I Suspect That This Question Can Be Better Articulated As:
Related Post: